Medical documentation plays a significant role in physicians’ day-to-day work. Cleaning up notes and completing clinical documentation after patient encounters, reviewing lab results, submitting prescription orders, responding to patients’ messages—these are the nuts and bolts of providing care, even though the work is not flashy. Recording all this information thoroughly and accurately leads to many benefits, for both patients and providers.
However, it seems that the time needed to complete these important tasks is becoming unsustainable, stretching into “pajama time”—according to new research from athenahealth, 69% of physicians report spending too much time after-hours on clinical documentation in electronic health records.1 This seemingly unsurmountable workload is taking a toll. Today, 62% of physicians identify “excessive documentation requirements” as their leading cause of burnout.2
Clinical documentation improvement is a problem that should be addressed. The quality and accuracy of your documentation, in its various forms, may have direct impacts on the quality of care you provide, the efficiency of your clinical and administrative processes, and even your rates of reimbursement. Let’s take a closer look at the challenge of manual EHR documentation, and how emerging technologies promise to help.
Manual documentation work is overwhelming physicians
When most people think about healthcare, the image in their mind is likely that of a physician and patient in an exam room, engaged in a detailed conversation about specific health concerns, discussing options for a care plan, or simply checking in. However, this crucial piece of the picture represents only a small portion of the time physicians spend doing their jobs.
Beyond patient encounters, physicians are deeply involved in the tracking and sharing of healthcare information. Getting clinical notes documented during and after an encounter is crucial for many reasons, primarily as a means to facilitate and inform future care.
The hard truth is that completing this type of healthcare documentation has historically been very manual and time-consuming, whether notes were handwritten in paper records or entered into electronic medical records systems. Clinical documentation is tedious, solitary work, but it’s necessary.
Thankfully, there’s evidence that both physicians and patients are hopeful that applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare will ease administrative burdens and support better care. For instance, a majority of physicians (83%) see potential benefits from AI in healthcare3, and 52% of patients believe AI will be part of the solution for healthcare’s current challenges.4
That’s hopeful news. But what does AI in healthcare look like, especially when it comes to documentation? Let’s take a look at AI-enabled medical documentation today, and what it might look like a few years down the road.
What does AI-enabled clinical documentation look like today?
Many practices leveraging innovative healthcare IT technology are already finding success with AI-enabled medical documentation tools and services. These include technologies like dictation tools for clinical documentation and mobile-optimized voice assistant tools. And, some clinics are beginning to experiment with emerging technologies like ambient clinical documentation.
How do those tools work, and what benefits are they delivering?
Reduce clinical documentation burden with AI-enabled dictation
Many healthcare IT platforms now include integrated and AI-enabled dictation tools. These tools enable you to use your speaking voice to document patient encounters. Using sophisticated innovations like natural language processing and machine learning, speech-to-text applications can quickly build a voice profile, enabling spoken words to be recorded and transcribed into clinical documentation, often at a very high rate of accuracy.
This automation can be beneficial during patient encounters because it removes multiple barriers––mostly hardware—that come between a physician and patient in the exam room. Using an AI-enabled dictation tool can help keep you in the flow of conversation and focused on your patient. And, it can help add a layer of transparency—instead of typing long, complex notes into text fields, you can simply state the information you want to document for both you and your patient to hear.
Dictation tools have significant benefits outside the exam room, as well. As physicians contend with time consuming tasks that stretch into the evening hours, even small applications of automation can make a big difference.
For instance, research has shown that using speech-to-text tools on mobile devices is three times faster than using a keyboard to type text, and with a 20% lower error rate.5 That could result in significant time savings for documentation work that is done away from patients, like in your office or at home.
In addition to time savings, dictation tools can also help with accuracy. It may seem counterintuitive at first—isn’t typing more accurate, even if it’s slower? The reality is that natural language processing tools have become so sophisticated in recent years that the opposite is now true. The technology can document your spoken words more quickly and accurately than you can type them.
Taken together, these benefits in efficiency and accuracy can also positively impact revenue. For example, accurate documentation of hierarchical condition categories and other clinical information lead to faster, more accurate reimbursements. This can be especially beneficial for clinicians utilizing value-based programs with stringent documentation requirements.6
Voice assistant tools to improve clinical documentation
Voice assistant tools are another technology tool being used to great success by physicians looking to make their documentation tasks more accurate and efficient.
Virtual voice assistants use natural language processing (similar to AI-enabled dictation tools) to enable navigation throughout your healthcare IT platform and performance of key tasks, all with the sound of your voice. For instance, a physician can open the mobile version of their healthcare IT platform during their commute and ask it to plan their day based on appointments. Or, a clinician may ask the voice assistant to retrieve certain clinical information while they’re with a patient for quick and easy retrieval that doesn’t require disruptive time in front of a computer screen.
Convenience and efficiency are the two most direct benefits that voice assistants offer. If used correctly, a voice assistant should enable you to spend less time at your computer and more time interacting with patients, or simply enjoying more down time outside the office.
Looking ahead to other emerging applications of AI in healthcare documentation
Like many AI-enabled tools and services, these innovations in clinical documentation are impressive in the accuracy with which they operate, and the efficiencies they can deliver. Even so, the industry is still just discovering how these powerful technologies can be applied, and which challenges they are best suited to solve.
- Provider action prediction: One such application is provider action prediction. Using predictive analytics and/or machine learning, technology platforms with EHR capabilities can analyze historical data and identify patterns to predict the actions a physician is most likely to take and recommend that action. Not only does provider action prediction save time, it also elegantly leverages data analytics within a workflow to potentially improve patient outcomes.
- Deduplication of data: Another useful application of automation is the cleaning and reconciliation of data within a patient’s medical history. For example, some healthcare platforms with EHR capabilities are adding back-end automation to scan patients’ records for duplicate information, like medications. This type of automation helps ensure medical records are accurate and up-to-day, and that data errors don’t result in errors in medication administration.
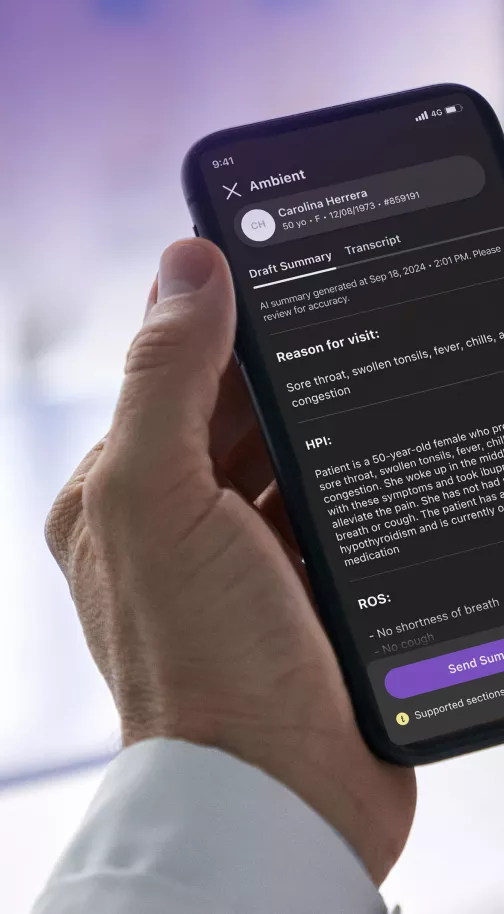
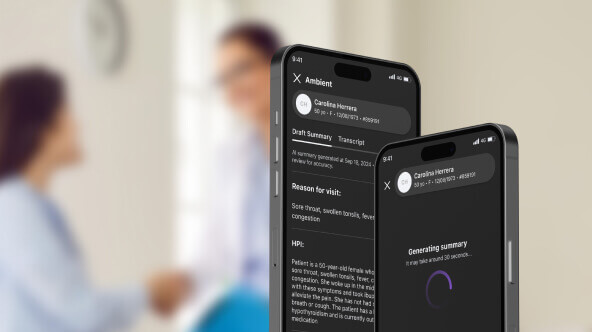
- Ambient documentation: One of the most promising services emerging from AI-enabled documentation technology is ambient documentation. Ambient documentation is, in some ways, the natural next step beyond the dictation tools described above. Ambient clinical documentation uses hardware like discrete, sensitive microphones to capture and record documentation on behalf of the physician, in real time. As the technology progresses, it will be able to capture information accurately, determine which information is most vital to record, and store it in the correct location. Not only does this high level of automation deliver significant efficiency benefits, but it also has the potential to improve patient-physician interactions by enabling crucial record keeping without the need to pause conversation or break eye contact.
Ambient medical documentation capabilities are not widely available today, but the technology is being tested and optimized by industry trailblazers. These clinical documentation improvement tools should be widely available within the next few years.
The benefits of AI in healthcare: We’re only getting started
The healthcare industry is in the early stages of leveraging the rapidly evolving field of AI and applying it to solve the many manual and data-related challenges that are causing burnout in all corners of the field. That said, certain AI-enabled tools for dictation and platform navigation are already delivering value and saving clinicians precious time, and other emerging tools like ambient documentation should begin adding value before long. Physicians looking to solve their efficiency challenges and curb the burnout it causes should explore the AI-enabled healthcare documentation tools at their disposal and look to technology partners to fill in the gaps.
Click the links below to learn more about how technology is addressing physician burnout.
As clinician burnout rises, how can technology help?
Managing patient communication to reduce physician burnout
How to improve healthcare operations to ease administrative burden
2023 Physician Sentiment Survey, commissioned by athenahealth and fielded by Harris Poll, Jan 2024
Ibid
Ibid
Patient Perception of AI, commissioned by athenahealth and fielded by Dynata, Nov 2023
Stanford, Aug. 2016, Speech Is 3x Faster than Typing for English and Mandarin Text Entry on Mobile Devices; https://hci.stanford.edu/research/speech/paper/speech_paper.pdf
TechTarget, What Are the Benefits of Clinical Documentation Improvement (CDI)? Feb. 2022; https://www.techtarget.com/searchhealthit/feature/What-Are-the-Benefits-of-Clinical-Documentation-Improvement-CDI