What is revenue cycle management?
In healthcare, revenue cycle management (RCM) refers to the process of managing and optimizing the financial aspects of a healthcare organization, from the initial patient encounter to the final payment. The healthcare revenue cycle consists of a series of steps that must be completed efficiently and accurately so payment can be received.
What is the goal of revenue cycle management?
The goal of revenue cycle management is to ensure accurate and timely reimbursement for the healthcare services a practice provides. In an optimized healthcare revenue cycle, payers and patients are accurately billed for the appropriate services, and practices get paid what they’re owed on time.
What are the steps in a healthcare revenue cycle?
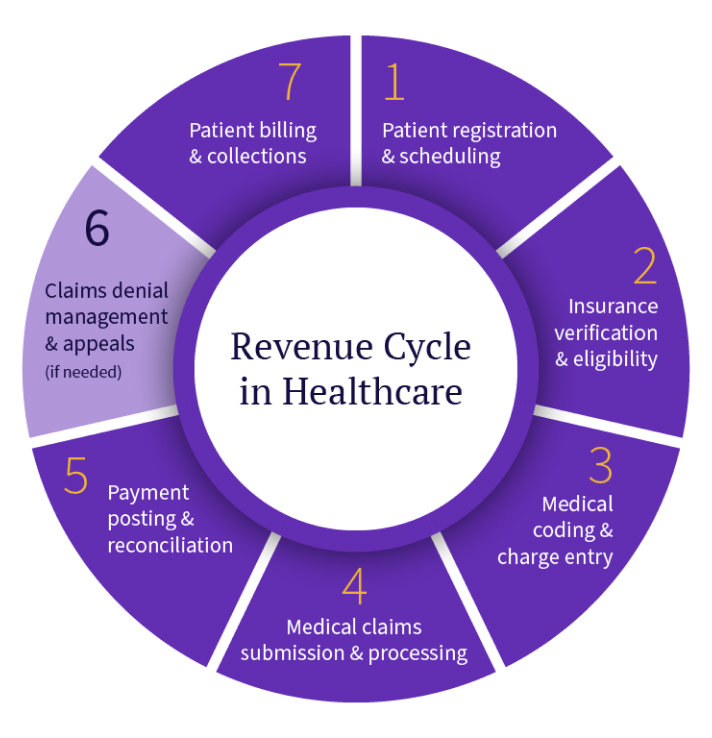
As the name implies, the revenue cycle in healthcare is cyclical, with one step leading to the next before starting over again.1 Here are the key steps in the process for healthcare organizations:
1. Patient registration and scheduling
The first step in a healthcare revenue cycle is registering new patients, updating their records, and scheduling an appointment for service. This step is crucial for ensuring the practice has accurate and up-to-date information about the patient necessary for treatment, billing, and reporting.
Scheduling is simply the process of setting up appointments for patients to receive services. This may be done by front-office staff, or via a patient portal or app. Scheduling is important in the revenue cycle because maintaining an optimum schedule density enables physicians to spend their desired about of time with patients, while also seeing as many patients as possible throughout the day. Strategic scheduling helps with revenue and can also help improve health outcomes by supporting continuous patient care.
2. Insurance verification and eligibility
The next step in a healthcare revenue cycle is verifying a patient’s insurance. It’s important for providers to know that the patient has an active insurance policy and what the terms of coverage are, since this matters for how much your practice will be reimbursed for services. It also helps prepare the patient for how much they will have to pay out of pocket; it’s always best to inform them up front, before services are provided.
Determining insurance verification and eligibility can be cumbersome when done manually because of the level of data extraction. That’s why athenaOne® utilizes AI for Optical Character Recognition (OCR). The AI in the Automated Insurance Selection workflow selects appropriate coverage from an uploaded insurance card, helping to drive a 12.8% reduction in patient insurance-related denials for claims submitted using the AI-powered Automated Insurance Selection workflow.2
The Automated Insurance Selection workflow and AI OCR don’t just save time for practice staff, but can also help improve accuracy at the very start of the RCM process.
3. Medical coding and charge entry
After services are provided, they must be properly coded. Medical coding involves translating medical procedures, diagnoses, and services into standardized codes for billing and reimbursement purposes. This may be done manually by a medical coder or automated to some degree by a healthcare IT platform. For instance, some integrated healthcare platforms enable providers to select pre-populated codes during a patient encounter or use language processing-enabled tools to scrape clinical documentation and produce codes automatically. athenaOne will offer AI-enabled Express Coding to help generate accurate claims—including the correct codes and modifiers—while Clinical Documentation Improvement (CDI) will provide nudges for clinicians reminding them to complete all necessary documentation.
Charge entry is the process of entering the coded information into your organization's billing system. Proper charge entry is necessary to reduce the risk of claim denials, underbilling, or overbilling.
4. Medical claims submission and processing
Once claims are properly coded, they can be submitted to the insurance provider for reimbursement. Submitting claims is now often done electronically, typically via a revenue cycle management platform, or with the help of a clearinghouse service. This is also an area where innovative technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning are adding value. For instance, athenaOne users benefit from the knowledge and data gained serving over 150,000 providers on the athenaOne network,3 who collectively submit more than 290 million claims annually.4
Native AI within the Advanced Intelligence Layer in athenaOne constantly structures and updates the data, with forthcoming AI-assisted payer knowledge and accelerated rules development also working to help anticipate changes in payer rules. This has led to an industry-leading clean claim submission rate of 98.4%.5
Submitting accurate, clean claims helps the revenue cycle tremendously because it means claims are typically approved the first time, shortening the overall cycle, reducing subsequent work, and improving the bottom line. By offering AI-enabled coding and AI-assisted payer knowledge, athenaOne helps streamline this step of the revenue cycle while reducing the chances of denials.
5. Payment posting and reconciliation
Payment posting is the recording and reconciling of payments received from insurance companies and patients for the healthcare services provided to a patient. Reconciliation involves comparing the recorded payments with the expected payments to ensure accuracy and to identify any discrepancies. These processes are crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring that all payments are properly accounted for in the healthcare organization's revenue cycle. This work doesn’t necessarily need to be done with in-house resources. For example, some technology platforms like athenaOne offer services to take on this kind of work and ensure the verified data is populated in the system.
6. Claims denial management and appeals
However, the ultimate goal is to avoid claim denials whenever possible. This can be done proactively with the help of a platform with RCM capabilities like athenaOne, or with services like athenaOne’s Enhanced Claim Resolution, which reviews claims and resolves issues before submission, and analyzes, addresses, and resolves any denials that do occur. The service is fully integrated with the athenaOne platform.
If a claim is denied, athenaOne will soon have a Denial Resolution capability that helps automate the resolution of coding-facing denials. This will include resubmitting the denied claim without the need for manual work.
7. Patient billing and collections
After the insurer has paid the claim, there may be an additional balance for the patient’s deductible, coinsurance, or copayments, according to their policy. Many practices collect copays at the time of service, since those are known during the insurance verification step. Doing this helps the practice collect a portion of the revenue right away and reduce the need for sending bills afterward.
Why is optimizing the healthcare revenue cycle important?
Revenue cycle management is an important process for healthcare organizations for a variety of reasons, including:
- Building and maintaining financial strength and stability for the long-term
- Improving cash flow so practices can meet their financial obligations
- Increasing revenue capture
- Supporting regulatory compliance with healthcare policies and guidelines
- Establishing operational efficiencies
- Enhancing patient experiences that keep patients coming back.
Thankfully, these great benefits can be achieved by healthcare organizations that understand the specific RCM-related challenges they face. Effective use of AI RCM technology can help solve those challenges by optimizing the revenue cycle faster, which can contribute to more complete reimbursements and a stronger bottom line.
At athenahealth, we strive to deliver solutions that can help reduce administrative burden and burnout while still helping practices maximize financial gains. That’s why we’re committed providing an AI-native, end-to-end RCM platform that offers smart, automative tools at every phase of the revenue cycle and continuously learns from updates across the network.
Reach out to one of our healthcare IT specialists to learn more about how healthcare practices of all kinds are leveraging the athenaOne® all-in-one solution for revenue cycle management, electronic health records, and patient engagement to deliver exceptional, patient-centric care while achieving business success.
More RCM resources
Continue exploring
- RevCycleIntelligence, What is Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management?, Feb. 2022. https://revcycleintelligence.com/features/what-is-healthcare-revenue-cycle-management
- Based on athenahealth data for 12 months ending June 2025. athenaOne customers who created claims with new insurance policies selected using the Automated Insurance Selection workflow saw a 12.8% reduction in patient insurance-related denials on those claims compared to those using other methods; M236
- Based on athenahealth data as of Dec. 2023; M010
- Based on athenahealth data for twelve months ending Dec. 2023; M016
- Based on athenahealth data for 12 months ending March 2025; results compared to competitors' self-reporting of clean claim submission rates; M164
Note: some content was updated in October 2025 for accuracy and relevance.










