How telehealth can improve chronic care and patient outcomes

Over the past several years, the COVID-19 pandemic greatly accelerated the adoption of telehealth, offering healthcare providers innovative ways to deliver care while ensuring the safety of both patient and provider. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve and embrace value-based care models, it is crucial to determine how to optimally deploy telehealth.
This can be particularly important for chronically ill patients who require frequent interactions with their care managers. Telehealth can not only increase accessibility and convenience for patients, but also enhance care coordination and patient engagement, which improves overall outcomes and value-based care metrics. By integrating telehealth into the healthcare ecosystem, providers can better address patients’ complex needs while enhancing the overall quality and value of care.
Increasing patient touchpoints
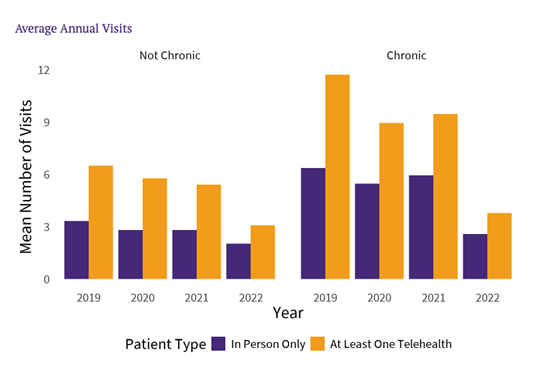
athenahealth network data shows that telehealth is an important form of access for chronic care patients, who are more likely to use telehealth than other patients — even after controlling for demographic factors. Telehealth patients tend to have more visits compared to those who do not utilize telehealth, and this is particularly true for patients with chronic conditions, who already see care providers much more frequently than patients without any chronic conditions. While this may seem like an increase in healthcare utilization, the hypothesis is that more frequent touchpoints can head off emergency department (ED) visits, increase patient engagement, and help ensure the right care is provided in the right way.
Improving outcomes for the chronically ill
Telehealth has emerged as a powerful tool for improving outcomes specifically in chronically ill patients. Unlike traditional, in-person healthcare, telehealth allows providers to bridge geographical barriers, streamline communication, and enhance patient engagement. As a virtual care solution, telehealth addresses many challenges faced by patients with chronic conditions, including access to care, medication management, and the need for ongoing support. In a recent athenahealth survey of telehealth patients, 23% of respondents indicated their telehealth visits were regularly scheduled check-ins related to chronic conditions, and 9% used it for ad hoc check-ins for chronic conditions (Source: 2022 athenahealth survey, fielded by Dynata, of 2,000 random adults).
"Telehealth may be making care more accessible to chronically ill patients, allowing them to have the care they need when and how they need it,” said Allison Roberts, Ph.D., athenahealth’s quantitative research manager.
Perhaps the foremost benefit of telehealth for chronically ill patients is the ease of access to healthcare professionals. By simply using their mobile phones, patients can conveniently connect with their care managers or specialists remotely, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits. This is particularly beneficial for patients with mobility issues, immunocompromised patients, those living in rural areas, or those with transportation challenges. Additionally, audio-only check-ins can be especially helpful for patients who might not always have access to reliable internet service.
Telehealth can also improve medication management, which is crucial for chronically ill patients. Care managers can proactively review patients' medication lists remotely to ensure they are taking their medications correctly while also identifying any potential drug interactions. By addressing these issues proactively, care managers are more likely to prevent complications that can sometimes arise from mismanagement of medications, or make timely changes in response to new health developments. For instance, a patient with congestive heart failure might have a telehealth check-in about sudden weight gain, allowing the care team to prescribe more diuretics to address increased fluid retention.
Reducing hospital visits
Another way telehealth can play a significant role in improving patient outcomes (all while reducing overall healthcare costs) is by helping care managers identify potentially serious health issues early on and address them before they escalate to a point where an ED visit becomes necessary. The ability to address health issues before they become serious can substantially reduce unnecessary hospitalizations, which reduces the burden on emergency departments and ultimately contributes to better risk adjustment factor (RAF) scores, which are crucial for value-based care reimbursement.
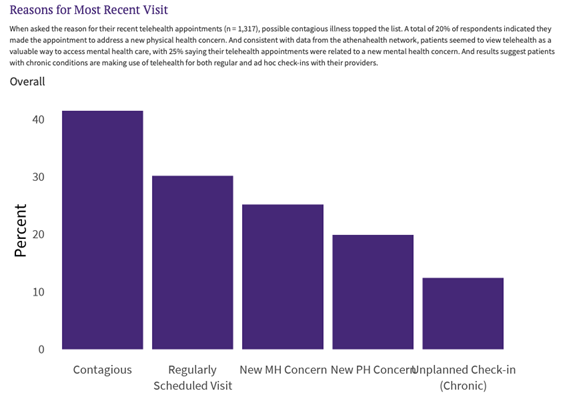
Our data supports the idea that patients are replacing costly care and avoiding unnecessary ED visits using telehealth. The chart above illustrates the reasons patients reported for their most recent telehealth visit (Source: 2022 athenahealth survey, fielded by Dynata, of 2,000 random adults). Telehealth enables care managers to connect with their patients remotely, making it easier to address questions or concerns that may arise between in-person visits, like contagious illness screening (the most common reason for using telehealth), newly arising mental and physical health concerns, or quick check-ins. In addition to avoiding unnecessary and expensive visits, telehealth also protects vulnerable patients. As the COVID-19 pandemic so clearly illustrated, the ability to keep contagious patients at home, while still providing the care they need, can protect other vulnerable patients and care providers from becoming ill. Finally, this virtual connection can facilitate a more personalized approach to care, empowering care managers to provide health education materials, discuss treatment plans, and monitor patients' progress more closely.
Collaborative support for social determinants of health
Telehealth has the potential to address social determinants of health (SDOH) in a unique and effective manner. By leveraging telehealth, care teams can better understand the SDOH that affect their patients and tailor solutions to help mitigate the negative effects of these factors on their overall health and well-being. For example, telehealth can give providers visibility into a patient’s home, which might enable them to assess safety risks such as trip hazards or even let them look at the contents of the patient’s refrigerator to make dietary recommendations.
Through virtual visits, care managers can observe patients' living conditions and gain insight into their daily challenges. This can help care managers identify potential barriers to care and develop strategies to overcome them. These strategies can include working with community and philanthropic partners to link patients with essential support services such as housing assistance, financial resources, and education programs. For example, if a patient has limited access to transportation, a care manager can connect them with a community resource that provides transportation services to medical appointments. This collaborative approach helps patients better manage their health and overcome barriers to care, which can ultimately lead to better patient outcomes, improved RAF scores, and financial performance in value-based care initiatives.
Leveraging telehealth to improve integration of behavioral health into patient care
Telehealth offers an innovative approach to integrating behavioral health into patient care by providing convenient and accessible mental health services alongside traditional medical care. Per a 2022 athenahealth patient survey, 23% of respondents reported they are more likely to seek mental health support because of its availability through telehealth (Source: 2022 athenahealth survey, fielded by Dynata, of 2,000 random adults). This integration is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions who often require ongoing support to manage both their physical and mental health needs.
The use of telehealth for behavioral health services eliminates common barriers to accessing mental health care, such as geographical limitations, long wait times, and stigma associated with in-person visits. Patients can connect with mental health professionals from the comfort of their own homes, creating a safe and private environment for addressing their concerns.
Because communication is more frequent and patients are typically more at-ease when receiving virtual care, telehealth can help patient and provider foster the rapport necessary to collaborate on comprehensive treatment plans that address both physical and mental health needs. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of a patient's well-being are considered and can lead to more effective and personalized care.
The ease of access to behavioral health services through telehealth can lead to early identification and intervention of mental health issues, preventing potential exacerbation of symptoms and the development of comorbid conditions. For instance, a patient who is managing their depression through active treatment is far more likely to be engaged and activated when it comes to their own overall healthcare. This can be particularly important in chronically ill patients. In turn, this proactive approach can improve overall patient outcomes and enhance the quality of care.
Overall, telehealth plays a pivotal role in integrating behavioral health into patient care by increasing accessibility, facilitating communication between providers, and promoting early intervention for mental health concerns. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, telehealth will remain a valuable tool for addressing the complex needs of patients and improving their overall well-being.
The future of value-based care
Telehealth has the potential to revolutionize the way care managers engage with and support their chronically ill patients, particularly within the context of value-based care. By providing a platform for addressing visit questions, health education, preventing ED visits, and collaborating with specialists, translators, and community partners, telehealth can contribute to improved patient outcomes and positively impact RAF scores.
Furthermore, telehealth enables care managers to address SDOH, integrate behavioral health into care management, and ultimately improve patient outcomes and value-based care success. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve and adopt value-based care models, leveraging the power of telehealth will be essential for strengthening and connecting the continuum of care and improving population health.